Category: Health and Wellness
-

“Breaking Fitness Plateaus: The Arnold-Approved Method to Progress – One More Rep at a Time!”
This article is from Arnold Schwarzenegger’s Pump Club email, 2024-March-05 Unlocking Progress with Arnold’s Proven Method Has your fitness progress hit a plateau? Here’s a method we learned from Arnold that can push you to become better. No matter what you do in any given workout, the goal of the next workout is to do…
-

Unlocking the Secrets of Omega-3s: Your Guide to Preserving and Gaining Muscle Health
Omega-3 fatty acids may play a crucial role in muscle maintenance and growth during inactivity, as suggested by recent research. Studies show taking EPA and DHA can prevent muscle loss over short periods and even increase muscle mass during extended periods of little movement. While particularly impactful for inactive individuals, the effects on active people…
-

Unraveling the Facts About Chemical Levels in Cheerios
Research disputes claims of hazardous chemical levels in Cheerios, emphasizing that one would need to consume an implausible quantity to encounter health risks. Dr. Love notes that the body quickly eliminates the pesticide chlormequat, and risks from everyday consumption are negligible. The article encourages informed decisions based on scientific insights rather than sensationalist headlines.
-

Optimizing Creatine Use: Debunking Myths and Choosing the Right Form
Arnold Schwarzenegger’s Pump Club recommends creatine monohydrate for its multitude of benefits, debunking bloating myths and emphasizing its superior absorption over other forms. Dosage should align with goals: 5 grams for muscle, 10 grams for cognitive enhancement.
-
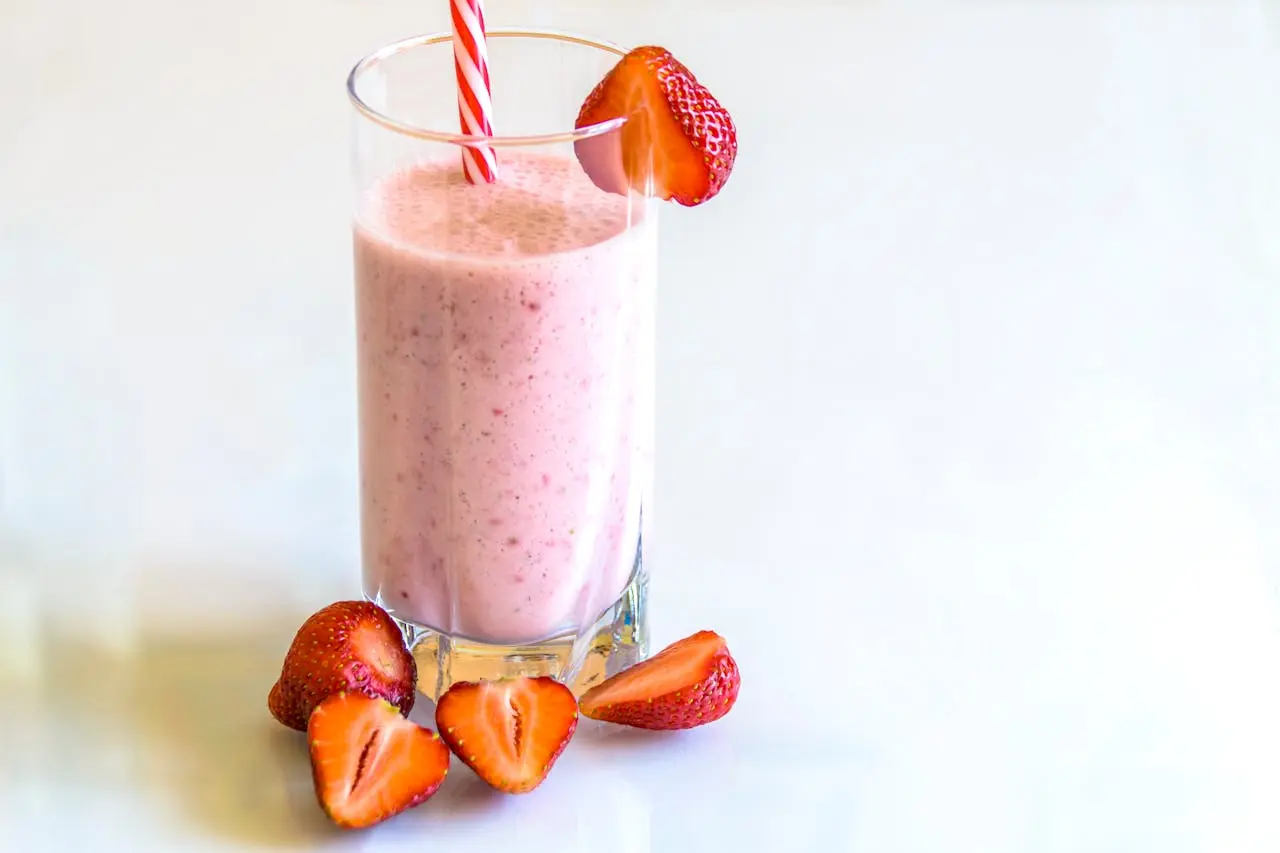

Unlock Your Nutrient-packed Potential: Pump Club-Approved Smoothie Recipe with Arnold Schwarzenegger’s Wellness Wisdom
Arnold Schwarzenegger’s “Pump Club” email suggests incorporating fruits and vegetables into meals by adding them to sandwiches, soups, or smoothies. A recommended smoothie recipe is provided, featuring blueberries, strawberries, protein powder or Greek yogurt, milk, ice, and an optional spinach addition for extra nutrients.
-

Debunking the 20-Gram Myth: Unleashing the Power of Protein Absorption in Your Muscles
A new study challenges the notion that the body can only use 20 grams of protein post-workout, suggesting a capability for utilizing much higher amounts for muscle synthesis over 12 hours. Arnold Schwarzenegger’s email highlights this research, noting meal frequency is less important than total protein intake for achieving fitness goals, while recognizing the need…